
Your VTAM administrator and your host system administrator must configure VTAM and OS/390 (or MVS/ESA) to prepare DB2 for OS/390 (or DB2 for MVS/ESA) to receive inbound connection requests from your DB2 Connect workstation.
This section provides:
For a summary of the example VTAM names used throughout this book, see "Sample Network Element Names (VTAM)". For TCP/IP names, see "Configuring TCP/IP for DB2 for OS/390".
| Note: | If you will use the LU6.2 Syncpoint Manager (SPM) function of DB2 Connect Enterprise Edition for AIX or OS/2, it is particularly important to read Chapter 22. "Setting Up Two-phase Commit Using SNA". The examples documented here do not include the additional steps required to set up the SPM. |
In order to prepare DB2 for OS/390 or DB2 for MVS/ESA to receive connection requests from DB2 Connect, you must complete the following steps at your DB2 for OS/390 host:
VTAM needs to be configured only if DB2 Connect will use SNA connections; it is not required if DB2 Connect will only use TCP/IP database connections (see "Configuring TCP/IP for DB2 for OS/390").
To configure VTAM, your VTAM Administrator needs to determine the names and options to be used on your system. The following definitions must be provided to enable the DB2 Connect workstation to connect to the host:
| Note: | If you are using SNA two-phase commit, the LU definition must be the name defined at the DB2 Connect server using the SPMNAME database manager configuration parameter. |
The VTAM sample definitions are provided in the sections that follow. These samples use parameters that match the parameters used elsewhere in this book.
All the examples in this section use the same names as elsewhere in this book, as shown in Figure 26:
Figure 26. Network Element Names Used in the VTAM Examples
DB2 Connect GATEWAY:
- Network ID : SPIFNET
- Local Node Name : NYX1 (PU name)
- Local Node ID : 05D27509
- LU Name : SPIFNET.NYX1GW01 (the same LU is used
for DB2 Connect,
for DB2 Universal Database DRDA-AS,
and for the SPM)
- LU Alias : NYX1GW01
HOST:
- Network ID : SPIFNET
- Node Name : NYX
- LU Name : SPIFNET.NYM2DB2
- LU Alias : NYM2DB2
- LAN Destination Address : 400009451902 (NCP TIC address)
MODE DEFINITION:
- Mode Name : IBMRDB
DB2 for MVS/ESA:
- Location : NEW_YORK3
SECURITY:
- Security Type : Program
- Authentication Type : DCS
|
In this scenario, both userid and password are checked only at the host. If you use Authentication SERVER, which is the default, then authentication will also take place at the DB2 Connect server.
| Note: | If you are using SNA two-phase commit, the LU Name must be the same as the SPM LU name at the DB2 Connect server. |
Figure 27 lists the sample VTAM application major node definition used for DB2 for OS/390 in this book. In most cases, such a definition will already exist with a different LU name.
Otherwise, this application major node must be defined, and DB2 for OS/390 must be customized in order to use the LU name defined. This name is the Partner LU name required by DB2 Connect.
Figure 27. Sample VTAM APPL Definition for DB2 for OS/390 or DB2 for MVS/ESA
----+----1----+----2----+----3----+----4----+----5----+----6----+----7--
DB2APPLS VBUILD TYPE=APPL
NYM2DB2 APPL APPC=YES, X
AUTH=(ACQ), X
AUTOSES=1, X
DLOGMOD=IBMRDB, X
DMINWNL=512, X
DMINWNR=512, X
DSESSLIM=2048, X
EAS=6000, X
MODETAB=RDBMODES, X
PARSESS=YES, X
PRTCT=SFLU, X
MODETAB=RDBMODES, X
SECACPT=ALREADYV, X
SRBEXIT=YES, X
VERIFY=NONE, X
VPACING=8
|
Notes:
SYNCLVL=SYNCPTThis enables Syncpoint support, which allows you to use two-phase commit over SNA connections to DB2 for OS/390.
Figure 28 lists the sample VTAM switched major node definition used for the example DB2 Connect workstation in this book.
If you already use SNA applications on the DB2 Connect workstation, then a PU definition already exists. However, an independent LU definition might not. The independent LU definition required for DB2 Connect must have LOCADDR=0 specified.
Figure 28. Sample VTAM Switched Major Node Definition for DB2 Connect
----+----1----+----2----+----3----+----4----+----5----+----6----+----7--
SWITCHED MAJOR NODE DEFINITION FOR PU NYX1 and
INDEPENDENT LU NYX1GW01
LOC300 VBUILD TYPE=LOCAL
NYX1 ADDR=01,IDBLK=071,IDNUM=27509,ANS=CONT,DISCNT=NO, X
IRETRY=YES,ISTATUS=ACTIVE,MAXDATA=4302,MAXOUT=7, X
MAXPATH=1,PUTYPE=2,SECNET=NO,MODETAB=RDBMODES X
SSCPFM=USSSCS,PACING=0,VPACING=2
NYX1GW01 LOCADDR=000,MODETAB=RDBMODES,DLOGMODE=IBMRDB
OTHERLU LOCADDR=002
|
Alternatively, you can enable DYNPU and DYNLU in VTAM to allow any PU and LU access through VTAM.
Figure 29 lists the sample VTAM logon mode table definition IBMRDB used in this book. Note that this example specifies a 4K RUSIZE, which may not be suitable for your environment (for example, if you are using Ethernet, which has a maximum Frame Size of 1536 bytes). Your VTAM Administrator should check these values and advise you which mode table entry name and RUSIZE to specify for DB2 Connect.
Figure 29. Sample VTAM Log Mode Definition for DB2 Connect
----+----1----+----2----+----3----+----4----+----5----+----6----+----7---
RDBMODES MODTAB
IBMRDB MODEENT LOGMODE=IBMRDB, DRDA DEFAULT MODE *
TYPE=0, NEGOTIABLE BIND *
PSNDPAC=X'01', PRIMARY SEND PACING COUNT *
SSNDPAC=X'01', SECONDARY SEND PACING COUNT *
SRCVPAC=X'00', SECONDARY RECEIVE PACING COUNT *
RUSIZES=X'8989', RUSIZES IN-4K OUT-4K *
FMPROF=X'13', LU6.2 FM PROFILE *
TSPROF=X'07', LU6.2 TS PROFILE *
PRIPROT=X'B0', LU6.2 PRIMARY PROTOCOLS *
SECPROT=X'B0', LU6.2 SECONDARY PROTOCOLS *
COMPROT=X'D0B1', LU6.2 COMMON PROTOCOLS *
PSERVIC=X'060200000000000000122F00' LU6.2 LU TYPE
SNASVCMG MODEENT LOGMODE=SNASVCMG, DRDA DEFAULT MODE *
PSNDPAC=X'00', PRIMARY SEND PACING COUNT *
SSNDPAC=X'02', SECONDARY SEND PACING COUNT *
SRCVPAC=X'00', SECONDARY RECEIVE PACING COUNT *
RUSIZES=X'8585', RUSIZES IN-1K OUT-1K *
FMPROF=X'13', LU6.2 FM PROFILE *
TSPROF=X'07', LU6.2 TS PROFILE *
PRIPROT=X'B0', LU6.2 PRIMARY PROTOCOLS *
SECPROT=X'B0', LU6.2 SECONDARY PROTOCOLS *
COMPROT=X'D0B1', LU6.2 COMMON PROTOCOLS *
PSERVIC=X'060200000000000000000300' LU6.2 LU TYPE
|
Note that you must define SNASVCMG when using APPC.
Before you can use DB2 Connect, your DB2 for OS/390 Administrator must configure DB2 for OS/390 to permit connections from the DB2 Connect workstation. This section indicates the minimum updates required in order to permit the DB2 Connect Application Requester to make a connection to DB2 for OS/390. More detailed examples can be found in DB2 Connectivity Supplement, and DB2 for OS/390 Installation Reference.
The following tables need to be updated, depending on the type of connections you are using (SNA or TCP/IP):
The sections that follow contain examples of commands to update these tables for DB2 for OS/390. Work with your DB2 Administrator to determine the updates required for your DB2 for OS/390 system. The DB2 for OS/390 Communications Database tables are described in DB2 for OS/390 SQL Reference.
To permit database connection requests to be accepted from any incoming DB2 Connect LU, just insert a blank row. Use an SQL command such as the following:
INSERT INTO SYSIBM.LUNAMES (LUNAME) VALUES (' ')
Alternatively, if you want to restrict access by LU name, you can use an SQL command such as the following to update this table:
INSERT INTO SYSIBM.LUNAMES (LUNAME,
SECURITY_OUT,
ENCRYPTPSWDS,
USERNAMES)
VALUES('NYX1GW01','P','N','O');
Result:
COLUMN EXAMPLE REMARK ====== ======= ====== LUNAME NYX1GW01 Name of the DB2 Connect LU SECURITY_OUT P ENCRYPTPSWDS N USERNAMES O
If you want to permit inbound database connection requests for TCP/IP nodes, you can use an SQL command such as the following to update this table:
INSERT INTO SYSIBM.IPNAMES (LINKNAME) VALUES(' ')
Before you can use the DB2 Connect connection, your DB2 for MVS/ESA Administrator must configure DB2 for MVS/ESA to permit connections from the DB2 Connect workstation. To configure DB2 for MVS/ESA, the following tables need to be updated:
The sections that follow contain examples of commands to update these tables. Work with your DB2 Administrator to determine the options required for your DB2 for MVS/ESA system.
If you want to use secondary authorization IDs, you can use the following SQL command to update this table:
INSERT INTO SYSIBM.SYSUSERNAMES VALUES('I','ADBUSER','NYX1GW01',' ',' ');
Result:
COLUMN EXAMPLE REMARK ====== ======= ====== Type I Authid ADBUSER LU Name NYX1GW01 Name of the DB2 Connect LU NewAuthID (blank) Password (blank)
USERNAME types are: O (outbound translation), I (inbound translation), B (both inbound and outbound) and blank (no authorization ids are translated, and no password is sent to the server).
If you want to restrict access by LU name, you can use an SQL command such as the following to update this table:
INSERT INTO SYSIBM.SYSLUNAMES VALUES('NYX1GW01','IBMRDB','A','N',' ','I');
Result:
COLUMN EXAMPLE REMARK ====== ======= ====== LUNAME NYX1GW01 Name of the DB2 Connect LU SYSMODENAME IBMRDB USERSECURITY A ENCRYPTPSWDS N MODESELECT USERNAMES I
Alternatively, just insert a blank row, and this will allow any incoming DB2 Connect LUs to be accepted.
You can use an SQL command such as the following to update this table:
INSERT INTO SYSIBM.SYSLUMODES VALUES ('NYX1 ', 'IBMRDB', 150, 'Y');
where:
This section tells you how to configure TCP/IP communications between your DB2 Connect workstation and DRDA servers running DB2 for OS/390 Version 5.1. It assumes that:
| Note: | If you want to know how to set up DRDA two-phase commit over
TCP/IP connections, see Chapter 23. "Setting up Two-phase Commit using TCP/IP". This chapter also addresses some migration considerations.
Also, if you do not know this information for the OS/390 or MVS/ESA system that you are connecting to, consult your system administrator for:
|
Before you can use DB2 Connect over a TCP/IP connection, you must collect some information about both the DRDA host and the DB2 Connect workstation. For each DRDA host server that you are connecting to via TCP/IP, you must know in advance:
Refer to your local network administrator and your DB2 for OS/390 administrator for help getting this information. Use one copy of the example work sheet, Table 45, to plan each TCP/IP connection between DB2 Connect and a DRDA host server.
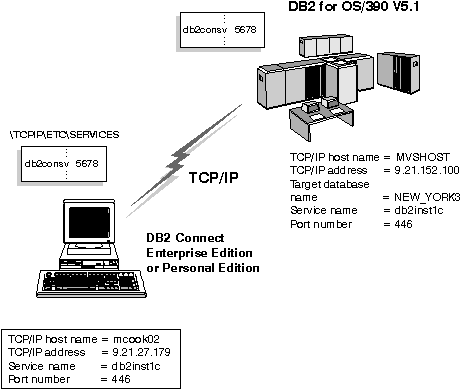
Figure 30 illustrates the example scenario. The values used in this diagram correspond to those used in Table 45.
Figure 30. Sample scenario for TCP/IP connection to DB2 for OS/390 host
 |
Table 45. Example Worksheet for Planning TCP/IP Connections to DB2 for OS/390
| Ref. | Description | Sample Value | Your Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| User Information | |||
| (TCP-1) | User Name | A.D.B.User |
|
| (TCP-2) | Contact Info | (123)-456-7890 |
|
| (TCP-5) | User ID | ADBUSER |
|
| (TCP-6) | Database Type | db2390 |
|
| (TCP-7) | Connection type (must be TCPIP). | TCPIP | TCPIP |
| Network Elements at the Host | |||
| (TCP-8) | Host name | MVSHOST |
|
| (TCP-9) | Host IP address | 9.21.152.100 |
|
| (TCP-10) | Service name | db2inst1c |
|
| (TCP-11) | Port number | 446 |
|
| (TCP-12) | Target database name | NEW_YORK3 |
|
| (TCP-13) | User ID |
|
|
| (TCP-14) | Password |
|
|
| Network Elements at the DB2 Connect Workstation | |||
| (TCP-18) | Host name | mcook02 |
|
| (TCP-19) | IP address | 9.21.27.179 |
|
| (TCP-20) | Service name | db2inst1c |
|
| (TCP-21) | Port number | 446 |
|
| DB2 Directory Entries (at the DB2 Connect workstation) | |||
| (TCP-30) | Node name | MVSIPNOD |
|
| TCP-31 | Database name | nyc3 |
|
| (TCP-32) | Database alias | mvsipdb1 |
|
| (TCP-33) | DCS database name | nyc3 |
|
| (TCP-34) | TM_DATABASE | 1ST_CONN (recommended) |
|
Notes:
TSO NETSTAT HOME
Use the manual steps in this section to complete the configuration and make the connection.
Complete a copy of the example worksheet for each TCP/IP host:
Note that some additional planning considerations may apply, for example if you are using DCE. See the DB2 Connect User's Guide.
At your DB2 for OS/390 host:
ping remote_host_name -p port_number
At your DB2 Connect workstation:
ping myhostThis will return the host address.
ping MVS_host_name -p port_number
At a command line prompt, issue the following command to update the Database Manager Configuration:
db2 update dbm config using tm_database "1st_conn"
where TM_DATABASE can have one of the following settings:
| Note: | TM_DATABASE cannot be left to default. If no TM_DATABASE value is provided then any CONNECT issued will fail with SQLCODE 865. If you want more information about TM_DATABASE options, refer to Administration Guide. If you want to know how to set up DRDA Two-phase commit over TCP/IP connections, refer to Chapter 23. "Setting up Two-phase Commit using TCP/IP". |
db2 catalog tcpip node MVSIPNOD remote MVSHOST server dbs2inst1cwhere:
db2 catalog dcs database NYC3 as NEW_YORK3 db2 catalog database NYC3 as MVSIPDB1 at node MVSIPNOD authentication dcswhere:
Finally, connect to the DRDA Server and bind the utilities and applications to the DRDA server using commands similar to the following in the command line processor:
connect to MVSIPDB1 user USERID using PASSWORD
bind path@ddcsmvs.lst blocking all
sqlerror continue messages ddcsmvs.msg grant public
disconnect all
These commands are described in detail in the Command Reference.