Installing and Configuring DB2 Clients
This section describes how to configure a client workstation to communicate
with a DB2 server using the APPC communication protocol, and assumes that APPC
is functional on the client and DB2 server workstations. See "Software Requirements" for the communication protocol requirements for your platform. See "Possible Client-to-DB2 Server Connectivity Scenarios" for the supported communication protocols for your particular client and
server.
|
You need to ensure that the DB2 server that you are attempting to establish
communications with supports APPC clients. APPC client communications
are supported by the following DB2 servers:
- AIX
- OS/2
- Solaris
- Windows NT
For more information, see "Software Requirements".
|
The following steps are required to set up a client to use APPC
communications:
- Identify and record parameter values.
- Configure the client:
- Update the APPC profiles.
- Catalog the APPC node.
- Catalog the database.
- Test the connection between the client and server.
As you proceed through the configuration steps, complete the
Your Value column in the following table. You can fill in
some of the values before you start configuring this protocol.
Table 19. APPC Values Required at the DB2 Client
| Parameter
| Description
| Sample Value
| Your Value
|
| Symbolic destination name (sym_dest_name)
|
Specifies the name of the CPI-C profile defined in SNA on the
client. The profile contains information that allows the client to
communicate with the server.
This profile name is used by DB2 as a link into the SNA communications
subsystem on your client. Obtain this name from your SNA System
Administrator or your SNA management tools.
| NYSERVER
|
|
| Security type (Security_type)
| Specifies the type of APPC security to be used for the connection.
It is recommended that you use the security level none for the APPC
connection. If you do not specify this parameter in "B. Catalog the APPC Node", the default program is used.
| none
|
|
| Node name (Node_name)
|
A local alias, or nickname, that describes the node where the database
resides. You can choose any name you want, however, all Node name
values within your local node directory must be unique.
| db2node
|
|
The following steps describe how to configure this protocol
on the client. Replace the sample values with your worksheet
values.
You must update the APPC communication profiles before your
client can access a DB2 server. Use the provided worksheet to help you
track values when updating the APPC profiles for your particular
client.
Table 20. APPC Values Required at the Client
| No.
| Description
| Sample Value
| Your Value
|
| Network Connection Information at the DB2 Client
|
| (13)
| Partner node name
| NYX1
|
|
| (14)
| Type
| Token-ring
|
|
| (15)
| Connection name
| LINKNYX1
|
|
| (16)
| LAN Destination Address
| 40005AA8B532
|
|
| (17)
| Partner network ID
| SPIFNET
|
|
| (18)
| Partner LU name
| NYX1GW01
|
|
| Network Elements at the DB2 Client
|
| (19)
| Network name
| SPIFNET
|
|
| (20)
| Local node name (same as the Control Point name)
| NYX2
|
|
| (21)
| Local node ID
| 05D27510
|
|
| (22)
| Partner LU fully-qualified LU name
| SPIFNET.NYX1GW01
|
|
| (23)
| Symbolic destination name
| NYSERVER
|
|
| (24)
| Partner TP name
| NYSERVER
|
|
| (25)
| Security type
| NONE
|
|
| (26)
| Mode name
| IBMRDB
|
|
| (27)
| Local LU name
| NYX2GW01
|
|

|
Go to the section that describes the required steps to update the APPC
profiles for the client that you want to use to communicate with you DB2
server.
|
You need to customize the APPC configuration for the client. The
following list gives the APPC profiles that you will need to update on your
client workstation before you can access a DB2 server using APPC.
- Control Point Profile
- Token Ring SNA DLC Profile
- Token Ring Link Station Profile
- LU 6.2 Mode Profile
- Partner LU 6.2 Location Profile
- LU 6.2 Side Information Profile
Samples of the profiles are provided. A field that has been changed
with the default value has been marked with a number in parentheses in each of
the sample profiles.
A worksheet is provided on Table 20. Each of the values marked with numbers in parentheses in the
following samples are included in the corresponding worksheet. Use the
worksheets to record the values of parameters that you need to provide when
you create or modify a profile.
Configure your DB2 Connect for AIX system as follows:
- Log on to the AIX machine as root.
- On the command line, enter:
smit
- Select panels in the following order:
- Communications Applications and Services
- SNA Server/6000
- Configure SNA Profiles
- Advanced Configuration.
The next several steps begin from the Advanced Configuration panel.
- Update the Control Point Profile as follows:
- Select the Control Point panel.
- Select the Change/Show a Profile panel.
- Between the square brackets [ ], enter the value of the XID
node ID (21).
The control point name was probably set when the SNA Server for AIX was
installed. (20).
To minimize confusion, use the same value for the control point alias as
for the control point name.
For example, the panel could look like this:
Change / Show Control Point Profile
*Profile name node_cp
XID node ID [05D27510] (21)
Network name [SPIFNET] (19)
Control Point (CP) name [NYX] (20)
Control Point alias [NYX2] (20)
Control Point type appn_end_node
Maximum number of cached routing trees [500]
Maximum number of nodes in the TRS database[500]
Route addition resistance [128]
- Check the Token Ring SNA DLC Profile as follows:
- Select the Links panel.
- Select the Token Ring panel.
- Select the Token Ring SNA DLC panel.
- Select the Change/Show a Profile panel.
- The profile name and data link device name were probably set when SNA
Server for AIX was installed. If you have a reason to change these
values, you can do so. If no values appear in the profile, talk to your
LAN administrator.
Write down the profile name.
For example, the profile might look like this:
Add Token Ring SNA DLC Profile
*Profile name [tok0.00001]
Data link device name [tok0]
Force disconnect time-out (1-600 seconds) [120]
User-defined maximum I-Field size? no
If yes, Max. I-Field size (265-30729) [30729]
- If you will use APPC for connections from remote clients, make sure that
the profile has the following value:
Dynamic link stations supported? yes
- Create a Mode Profile as follows:
- Select the Sessions panel.
- Select the LU 6.2 panel.
- Select the LU 6.2 Mode panel.
- Select the Add a Profile panel.
- Define your mode profile. For profile name and mode name, use the
value that you wrote in item (26) of the worksheet. On the other
lines, specify values that match the mode profile defined on your DRDA server
systems. If you are using the mode IBMRDB, specify the following
values:
*Profile name [IBMRDB] (26)
Mode name [IBMRDB] (26)
Maximum number of sessions (1-5000) [30] (*)
Minimum contention winners (0-5000) [15] (*)
Minimum contention losers (0-5000) [15] (*)
Auto activate limit (0-500) [0]
Upper bound for adaptive receive pacing window [16]
Receive pacing window (0-63) [8] (*)
Maximum RU size (128,...,32768: multiples of 32) [4096] (*)
Minimum RU size (128,...,32768: multiples of 32) [1024] (*)
Class of Service (COS) name [#CONNECT]
- Create a Local LU profile as follow:
- Select the Sessions panel.
- Select the LU 6.2 panel.
- Select the LU 6.2 Local LU panel.
- Select the Add a Profile panel.
- Update the three lines with the following value: Use (27) for
the all three lines. For example, the file could look like this:
Add LU 6.2 Local LU Profile
*Profile name [NYX1GW02] (27)
Local LU name [NYX1GW02] (27)
Local LU alias [NYX1GW02] (27)
Local LU is dependent? no
If yes,
Local LU address (1-255) []
System services control point
(SSCP) ID (*, 0-65535) [*]
Link Station Profile name []
Conversation Security Access List Profile name []
You need to customize the APPC configuration for the client. The
following list gives the APPC profiles that you will need to update on your
client workstation before you can access a DB2 server using APPC.
- Link Service
- Connection Service
- Local Node Service
- APPC Mode
- APPC Remote LU
- APPC Local LU
- CPI-C Symbolic Destination Name
To use APPC, SNAplus must be installed and configured on the client
workstation, and you must create an entry in the node directory.
- Configuring SNAplus for Client Workstation
- Before configuring the connection between the DB2 Client Application
Enabler for HP-UX workstation and the server, you will have to collect some
information from the network administrator.
This section will give you an example of how to use those values to
configure the SNA parameters on the DB2 Client Application Enabler for HP-UX
workstation. This is only an example; you should be familiar with SNA
and your own communications configuration in order to successfully configure
SNAplus for DB2 Client Application Enabler for HP-UX.
Refer to the HP-UX SNAplus Installation Guide, the HP-UX SNAplusLink
Administrator's Guide, the HP-UX SNAplus API Administrator's Guide,
and the HP-UX SNAplusLink Diagnostics Guide for more information about:
- Installing SNAplus
- SNA terms and concepts
- Configuring the SNA parameters
- Problem resolution.
- Description of the Example
- The following assumptions were made when configuring this system:
- The basic installation of the SNAplus package has been completed,
including the execution of the INSTALL_SNAP script.
- DB2 Client Application Enabler for HP-UX has been installed.
- The user is logged on as root.
Notes:
- The values provided are for the example only; you must substitute values
that are appropriate to your operating system.
- Get the correct values from your network administrator.
- Use the worksheet in Table 20 to assist you in gathering the information.
The names and addresses in this example are:
CP Name NYX2 (20)
Remote LINK ADDRESS 40005AA8B532 (16)
XID Node ID 05D27510 (21)
Network Name SPIFNET (19)
Local LU Name NYX2GW01 (27)
Remote LU Name NYX1GW01 (18)
Remote Transaction Program Name NYSERVER (24)
Mode Name IBMRDB (26)
- Configuring SNAplus
-
To configure SNAplus for DB2 Connect for HP-UX, log on as root and use
either the /opt/sna/bin/snapconfig program or the
/opt/sna/bin/X11/xsnapconfig program. Information about
these programs can be found in the HP-UX documentation. The following
steps describe how to use these programs to configure SNAplus for DB2 Connect
for HP-UX.
| Note: | These steps contain suggested values for configuration parameters. For
other parameters, use the SNAplus default values.
|
- Open the configuration file:
- Select File->Open
- Select Open running configuration file, then click on
OK.
- Select the links:
- Select Services->Links.
- Select the option marked NEW associated with the type of link
you want to use: Token Ring (LAN), SDLC, or QLLC, then select
Add. Enter a name for this link, for example,
TR1.
For Token Ring links, use the default Device Name and Port Number.
For SDLC and QLLC links, consult with your network administrator for the
appropriate values. When you have filled in the information, or chosen
to use the default values, click on OK followed by Done
to get back to the main screen.
- Select the connections:
- Select Services->Connections. Select the
option marked NEW corresponding to the value selected in the
previous step. For example, for Token Ring, select NEW next
to LAN. Enter a name for this connection. You may
optionally enter a description.
- Set Remote End to Host System and
Activation to On Demand. If you are connecting to
a machine other than a host system, select Peer Node instead of
Host System.
- Enter the first three characters of the XID Node ID in the first Node
ID to Send field. For example, enter 05D.
- Enter the SNA Physical Unit Number associated with your system in the
second Node ID to Send field. For this example, enter
27510.
- Leave the "Node ID to Receive" fields blank.
- Enter your SNA Network Name in the first field of the Full Control
Point Name. For this example, enter SPIFNET.
- Enter the Physical Unit Name associated with your HP computer in the
second field of the Full Control Point Name. For this
example, enter NYX2.
- Move the link you configured in the previous step from the Other
Links box to the Links Usable box.
- Select Parameters and enter any necessary connection
information. For Token Ring, enter the SNA Destination Address assigned
for the DB2RA server system in the Remote Network Address field and
leave the other fields with their default values. For this example, use
400011527509. For SDLC and QLLC connections, additional
information is required. Ask your network administrator for the
required values.
- Click on OK to return to the connection configuration panel,
then click on OK again, then DONE.
- Select the local nodes:
- Select Services->Local Nodes.
- Select NEW.
- Enter a name for the node and click on OK. You may
optionally enter a description for the node, but you must enter your network
name in the Name of Network field. For this example, use
SPIFNET for this value.
- Move the connection you created in the previous step from the
Available Connections box to the Connections Used box
using the Move button.
- Click on OK, then DONE.
- Select the modes:
- Select APPC->Modes.
- Select NEW.
- Enter IBMRDB in the Mode Name field, and optionally
enter a description.
- In the Connection box, highlight the connection you configured
above. Make sure that High priority mode is not
selected. The following configuration values are suggested:
- Session limit = 030
- Minimum contention winner limit = 015
- Partner minimum contention winner limit = 015
- Automatic activation limit = 001
- Max send RU length = 4096
- Max receive RU length = 4096
- Send and Receive Pacing Counts = 07
Other values can be left as defaults.
- Click on OK, then DONE.
- Select Remote LUs:
- Select APPC->Remote LUs.
- Select NEW.
- Enter the Remote LU Name as the LU alias, and click on
OK. For this example, use NYX1GW01 . You
may optionally enter a description of the remote LU.
- The Full network name field is made up of the SNA network name
in the first field and the Remote LU Name associated with the DB2RA server
database in the second field. For this example, use
SPIFNET.NYX1.
- Select Supports parallel sessions and No session level
security
- Click on OK, then DONE.
- Select Local LU:
- From the APPC menu, select Local LUs.
- In the Local Nodes box, select the node you configured
above.
- In the Configured LUs box, select NEW.
- For the APPC LU alias, enter your Independent LU Name; for this example,
it is NYX2GW01. You may optionally enter a description for
the Local LU.
- Make sure that the Full Network Name fields contain your
Network Name and your Independent LU Name. The LU number should be
000 for an independent LU.
- Change the Session Limit parameter to 030
- Make sure that you have selected the radio buttons to indicate that this
LU is in the pool of default LUs.
- Move the Remote LU you configured above from the Other Remote
LUs box to the Partner LUs box.
- Select Modes.
- Move the IBMRDB mode from the Other Modes box to the
Associated Modes box.
- Click on OK, then OK again, then
DONE.
- Select the Symbolic destination name:
- Select APPC->Sym Dest Name.
- Select NEW.
- Enter the Symbolic Destination Name you want to associate with the DRDA
server database and click on OK. You may optionally enter a
description. This name must match the sym_dest_name value you use to
catalog the APPC node.
- For the Partner LU type, make sure that Alias is
selected.
- In the Partner LU box, ensure that the Remote LU you
configured above is highlighted.
- In the Mode Name box, highlight IBMRDB.
- For the Partner TP name, use NYSERVER. In
this example it is an Application TP.
- For the Partner LU type, make sure that Alias is
selected.
- Click on Security and choose none (This does not mean that you
will have no security; you can specify the security type later, in the node
directory).
- When done, click on OK, then OK, then
DONE.
- Saving your configuration:
- From the File menu, select Save.
- Select Update running configuration file, then click on
OK. This saves your new configuration as the default,
running configuration.
Notes:
- You may need to stop and restart SNA for your configuration changes to
take effect.
- You may also need to contact your database or network administrators to
have your Local LU names added to the appropriate tables in order to access
the DRDA server database.
- Starting the SNAplus Subsystem
-
Use /opt/sna/bin/snapstart to start the SNAplus
subsystem. You can use /opt/sna/bin/snapstop to stop the
SNAplus subsystem first, if required.
To start the SNAplus connections you can use either the
/opt/sna/bin/snapmanage program, or the
/opt/sna/bin/X11/xsnapmanage program.
- From the Manage menu, select Services.
- Highlight the node you configured in the previous section, and select
start.
- Highlight the computer you want to start it on, then click on
OK.
- Highlight the connection you configured in the previous section, and
select start.
- Highlight the computer you want to start it on, then click on
OK.
You need to customize the APPC configuration for the client. The
following list gives the APPC profiles that you will need to update on your
client workstation before you can access a DB2 server using APPC.
- Local Node Characteristic Profile
- Token Ring or Other LAN Types DLC Adapter Parameters Profile
- Adapter List Profile
- Connection to a Peer Node Profile
- Partner LUs Profile
- Mode Definition Profile
- CPI Communications Side Information Profile
Begin to configure your DB2 Connect system with the following steps:
- Double-click on the Communications Server icon.
- Double-click on the Communications Manager Setup icon.
- On the Communications Server Setup panel, click on the Setup
push button.
- On the Open Configuration panel:
- Specify the name of an existing configuration file if you have one, or
provide a name for a new file to be created.
- Click on the OK push button to proceed to the Communications
Server Configuration Definition panel.
- The Configuration Definition panel opens.
- Select the Commonly used definitions radio button.
- In the Communications Definitions window, select the protocol that you
want to use. These examples use APPC APIs over
Token-Ring.
- Click on the Configure push button to proceed.
If this is a new configuration file, the next panel displayed will be the
APPC APIs over Token-Ring panel. Otherwise the next panel displayed
will be the Communications Server Profile List panel.
- The APPC APIs over Token-Ring panel opens.
- Enter your values for:
- Network ID (19)
- Local node name (20)
- Click on the End node push button that your network
administrator advises you to use.
|
You can select either the End node - to a network node server
radio button or the End node - no network node server radio
button. A network node server is used when many users are routed
through the same connection. The example here presumes no network node
server is used.
|
- Click on the Advanced push button. The Communication
Manager Profile List window opens.
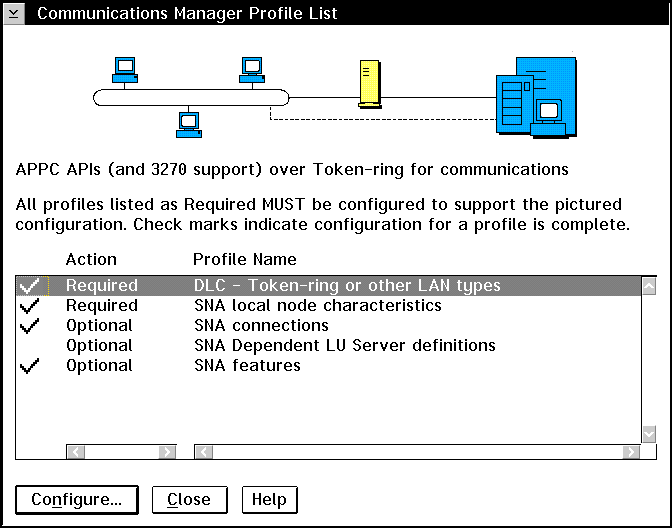
Subsequent steps begin from this panel. You will return to this
panel when each step is complete.
- LAN DLC Profile
-
From the Communications Server Profile List panel, prepare a LAN DLC
profile as follows:
- Select DLC - Token ring or other LAN
types->Configure.
- Enter your value for Network ID or C&SM LAN
ID.
- Check that the other values are appropriate for your environment.
The values in the example are default values.
- Click on OK to return to the Communications Server Profile List
panel.
- Local Node Characteristic Profile
-
Update SNA Local Node Characteristics as follows:
- On the Communications Server Profile List panel, select SNA local
node characteristics->Configure. The Local Node
Characteristic panel opens.
- Enter your value for Network ID (19).
- The Local node name was probably set when Communications Server
was installed. If you are not sure, consult your local network
administrator.
- Enter your value for Local node ID (hex) (21).
|
The first part should be filled in for you already when you display the
profile. You only need to complete the second part.
|
- Click on the Options push button. The Local Node Options
panel opens.
- Verify that the Activate Attach Manager at startup check box is
selected.
- Click on OK to return to the Local Node Characteristics
panel.
- Click on OK to return to the Communications Server Profile List
panel.
- Token Ring or Other LAN Types DLC Adapter Parameters Profile
-
- Adapter List Profile
-
Prepare the SNA connection profiles as follows:
- From the Communications Server Profile List panel, select SNA
Connections->Configure.
- On the Connections List panel for Partner Type, select the
To peer node radio button and click on the Create push
button.
- The Adapter List window opens.
- Select the Token-ring, or other LAN types adapter type, and
specify the same adapter number that you specified in the DLC
profile.
- Click on the Continue push button to proceed to the Connection
to a Peer Node panel or the Connection to a Host panel.
- Connection to a Peer Node Profile
-
The Connection to a Peer Node or Connection to a Host Node windows
opens. At the Connection to a Peer Node panel or the Connection to Host
panel:
- Specify the Link name value that you wrote in item (15)
of the worksheet.
- On the Connection to Host panel, select Additional parameters
push button and change the Local PU name field to your value for
(20).
- Change the node ID field to your values for (21).
- Change LAN destination address field to your value for .
- Change Partner network ID field to your value for
(17).
- Change Partner node name field to your value for
(18).
- Select Define Partner LUs push button on either the Connection
to a Peer Node panel or the Connection to Host panel to proceed.
- Partner LUs Profile
-
Create a Partner LUs Profile as follows:
- Enter your value for Network ID (17).
- Enter your value for LU name and Alias (use
(18)).
- Click on the Add push button to add the partner LU profile to
the connection profile.
- Click on OK to return to the previous panel.
- On the Connection to Host panel, click on the Additional
Parameters push button. The Partner LU window opens
- Mode Definition Profile
-
From the SNA Features List panel, prepare a Mode Definition as
follows:
- Select Modes->Create.
- Define your mode profile as follows:
- Enter your value for mode name (26).
- On the other lines, you can either specify values that match the mode
profile defined on your DB2RA server systems, or tune the parameters.
- Click on OK to finish the creation of the mode and to return to
the SNA Features List panel.
- CPI Communications Side Information Profile
-
On the SNA Features List panel, select CPI Communications Side
Information->Create. The CPI Communications Side
Information opens.
Complete the CPI Communications Side Information panel as follows:
- Enter your value for Symbolic destination name
(23).
- Select the Alias radio button. Click on the
Alias drop down box to view a list of all defined aliases and
choose the alias that corresponds to item (18).
- In the Partner TP box, specify the remote Transaction Program
(TP) name (24).
Select the None radio button as the Security
type.
|
This does not mean that you will have no security, you will specify the
security type later when you update the DB2 directories.
|
- Enter your value for the Mode name field (26).
- Click on OK to save the CPI side information profile and return
to the SNA Features List panel.
- Click on Close to return to the Communications Server Profile
List panel.
You need to customize the APPC configuration for the client. The
following list gives the APPC profiles that you will need to update on your
client workstation before you can access a DB2 server using APPC.
- Link Service Profile
- Connection Service Profile
- Local Node Service Profile
- APPC Mode Profile
- APPC Remote LU Profile
- APPC Local LU Profile
- CPI-C Symbolic Destination Name Profile
To use APPC, Interface Systems Cleo SNA must be installed and configured on
the client workstation, and you must create an entry in the node
directory.
- Configuring Interface Systems Cleo for the Client Workstation
-
Before configuring the connection between the DB2 Client Application
Enabler for SCO OpenServer workstation and the server, you will have to
collect some information from the network administrator.
This section will give you an example of how to use those values to
configure the SNA parameters on the DB2 Client Application Enabler for SCO
OpenServer workstation. This is only an example; you should be familiar
with SNA and your own communications configuration in order to successfully
configure Cleo for DB2 Client Application Enabler for SCO OpenServer.
Refer to the Interface Systems Cleo Administration Guide for
more information about:
- Installing Cleo
- SNA terms and concepts
- Configuring the SNA parameters
- Problem resolution.
- Enabling APPC Support
-
To use APPC, you must have the Interface Systems Cleo SNA, Version
4.1.1.0, installed and configured on the client .
- General Information about Configuring Interface Systems Cleo SNA
-
The following instructions can be used to guide you when configuring the
Interface System Cleo. Refer to the Interface Systems Connectivity
Solutions Cleo Administration Guide for specific configuration
instructions. The best way to configure Cleo SNA is in three
phases.
- Phase 1
-
In the first phase, you usually define a single LINK, a single NODE, and a
single CONNECTION. Run the Cleo SNA configuration program,
cxconfig, xcomconfig, or comconfig, to create
or change a configuration file.
Once a single connection becomes active, adding additional connections
becomes straight-forward.
- Phase 2
-
In the second phase, you define a LOCAL LU, a (remote) PARTNER LU, and a
MODE. A set of these three resources defines an APPC session.
|
If the mode enables parallel sessions, then multiple sessions can exist
simultaneously between the same LU pairs; this increases service
availability.
|
Once a session becomes active, adding additional Partner LUs and modes
becomes straight-forward.
- Phase 3
-
The third phase involves defining a CPIC Side Information profile and
differs depending on whether you are configuring a DB2 Client or a DDCS
workstation.
- Links, Connections and Nodes
-
This section gives more detailed information about links, connections, and
nodes required for Phase 1.
- LINK
-
A LINK describes the interface between Cleo and the hardware you use to
connect to the SNA network. This section assumes a correctly installed
hardware adapter. Consult the Cleo documentation for a list of
supported hardware adapters. You may give the link any name you
want. This name is not seen outside of the configuration or management
utilities of the Cleo SNA subsystem. For example, for a Token Ring
link, TOKLINK1, you identify the adapter device (the device driver) used for
that board. This can be determined from the SCO OpenServer command
llistat. A typical value is /dev/net0.
- CONNECTION
-
A CONNECTION is defined between your workstation and a remote computer, for
each remote computer you will be accessing. A connection uses a link to
reach the remote computer.
Typically, most of the difficulty is experienced with this resource, and in
particular, the node_id to send and to receive.
| Note: | For host connections, node ids may not be required at all, as explained in
the appropriate section of the Cleo Administration Guide.
Also, certain levels of VTAM may not require the node ids. You must
consult your VTAM administrator for an appropriate value in these
fields. The node id to send, if required, will come from the VTAM PU
macro describing your workstation, specifically fields IDBLK=xxx and
BLKNUM=yyyyy.
|
The node id to receive identifies the remote computer. It is usually
sufficient to code the xxx value of the remote node, and use "fffff" in the
BLKNUM field. A typical value for xxx is 05D.
You must also specify the MAC address of the adapter at the remote
computer. This address is entered under the Parameters
sub-window. This information must be supplied by your VTAM or Network
administrator.
- For host connections, this is the MAC address of the DB2 Connect
server.
- For Peer links, this is the MAC address of the peer computer.
| Note: | A host system typically controls hundreds to thousands of LUs. You
only need to define one connection to be able to access any of these
LUs. You may access multiple LUs over the same connection.
|
- NODE:
-
A Local NODE defines the local PU21 instance. There is one per
workstation. The node definition defines which links are active on the
node, and whether inbound connection requests will be allowed.
Once these three resources have been properly configured, a connection may
be started (or made active) using the Cleo management utilities.
- Local and Partner LUs and Modes
-
This section gives more detailed information about the modes and the local
and partner LUs that need to be defined for Phase 2.
- Define Mode
-
For DB2, use a mode name of "IBMRDB". See the worksheets for sample
values to use in the IBMRDB mode. Note that for host connections,
typically DDCS, there must be a corresponding VTAM MODEENT for the
MODE. Check with your VTAM administrator.
The mode entry in Cleo also defines which connection a session is
established over. You choose the connection needed by a particular
mode. This means that a) the connection must have been defined first,
and b), that multiple modes of the same name and characteristics must be
defined if you require connections to multiple remote databases at different
computers. It is recommended that you use the description field to
differentiate between each mode with the same name in this case (that is,
include the connection name in the Description field).
- Define Partner LUs
-
Your database administrator must provide you with the LU name of the
partner LU at the remote database. Each database you will access using
APPC will be defined to SNA with this LU name.
- Define a Local LU
-
Your VTAM administrator must give you the name of your local LU for
connections to the host. This LU must be defined to VTAM under the PU
macro defining your PU21 node. You must select which remote LUs will be
accessed from a particular local LU from the local LU definition panel and
also which node will be used for the session. Since the node defines
the connection that the session uses, you do not have to identify the
connection under the local LU definition. Note that each time you add a
remote partner LU definition, you must update the local LU definition to
include the new partner LUs. It is only necessary to define one local
LU for your workstation's SNA needs.
Once these three resources have been properly configured, a session may be
started (or made active).
| Note: | It is the ability to start connections and sessions without concern for
applications, that contributes to the high performance and reliability in APPC
SNA networks. If links, connections, and sessions are already active in
your workstation, then applications, such as DB2, will be able to start
LU6.2 conversations over those sessions with almost no delay for
resource acquisition and allocation.
A conversation is started when you issue the following DB2 SQL
statement:
connect to Database_name
|
- Description of the Example
- The following assumptions were made when configuring this system:
- The basic installation of the Cleo package has been completed.
- The user is logged on as root.
Notes:
- The values provided are for the example only; you must substitute values
that are appropriate to your operating system.
- Get the correct values from your network administrator.
- A worksheet is provided on Table 20 to assist you in gathering the information.
The names and addresses in this example are:
CP Name NYX2 (20)
Remote LINK ADDRESS 40005AA8B532 (16)
XID Node ID 05D27510 (21)
Network Name SPIFNET (19)
Local LU Name NYX2GW01 (26)
Remote LU Name NYX1GW01 (18)
Remote Transaction Program Name NYSERVER (24)
Mode Name IBMRDB (26)
- Configuring Interface Systems Cleo
-
To configure Interface Systems Cleo for use with DB2 Client Application
Enabler for SCO OpenServer, log on as root and use either the
/usr/bin/comconfig program or the /usr/bin/X11/cxconfig
program. Information about these programs can be found in the Cleo
documentation. The following steps describe how to use these programs
to configure Cleo for DB2 Client Application Enabler for SCO
OpenServer.
| Note: | These steps contain suggested values for configuration parameters. For
other parameters, use the Cleo default values.
|
- Open the configuration file:
- Select File->Open.
- Select Open running configuration file, then click on
OK.
- Select the links:
- Select Services ->Links.
- Select the option marked NEW associated with the type of link
you want to use: Token Ring (LAN), SDLC, or QLLC, then select
Add. Enter a name for this link, for example,
TR1.
For Token Ring links, use the default Device Name and Port Number.
For SDLC and QLLC links, consult with your network administrator for the
appropriate values. When you have filled in the information, or chosen
to use the default values, click on OK followed by Done
to get back to the main screen.
- Select the connections:
- Select Services->Connections. Select the
option marked NEW corresponding to the value selected in the
previous step. For example, for Token Ring, select NEW next
to LAN. Enter a name for this connection. You may
optionally enter a description.
- Set Remote End to Host System and
Activation to On Demand. If you are connecting to
a machine other than a host system, select Peer Node instead of
Host System.
- Enter the first three characters of the XID Node ID in the first Node
ID to Send field. For example, enter 05D.
- Enter the SNA Physical Unit Number associated with your system in the
second Node ID to Send field. For this example, enter
27509.
- Leave the "Node ID to Receive" fields blank.
- Enter your SNA Network Name in the first field of the Full Control
Point Name. For this example, enter SPIFNET.
- Enter the Physical Unit Name associated with your SCO OpenServer computer
in the second field of the Full Control Point Name. For this
example, enter NYX2.
- Move the link you configured in the previous step from the Other
Links box to the Links Usable box.
- Select Parameters and enter any necessary connection
information. For Token Ring, enter the SNA Destination Address assigned
for the DB2RA server system in the Remote Network Address field and
leave the other fields with their default values. For this example, use
400011527509. For SDLC and QLLC connections, additional
information is required. Ask your network administrator for the
required values.
- Click on OK to return to the connection configuration panel,
then click on OK again, then DONE.
- Select the local nodes:
- Select Services->Local Nodes.
- Select NEW.
- Enter a name for the node and click on OK. You may
optionally enter a description for the node, but you must enter your network
name in the Name of Network field. For this example, use
SPIFNET for this value.
- Move the connection you created in the previous step from the
Available Connections box to the Connections Used box
using the Move button.
- Click on OK, then DONE.
- Select the modes:
- Select APPC->Modes.
- Select NEW.
- Enter IBMRDB in the Mode Name field, and optionally
enter a description.
- In the Connection box, highlight the connection you configured
above. Make sure that High priority mode is not
selected. The following configuration values are suggested:
- Session limit = 030
- Minimum contention winner limit = 015
- Partner minimum contention winner limit = 015
- Automatic activation limit = 001
- Max send RU length = 4096
- Max receive RU length = 4096
- Send and Receive Pacing Counts = 07
Other values can be left as defaults.
- Click on OK, then DONE.
- Select Remote LUs:
- Select APPC->Remote LUs.
- Select NEW.
- Enter the Remote LU Name as the LU alias, and click on
OK. For this example, use NYX1 . You may
optionally enter a description of the remote LU.
- The Full network name field is made up of the SNA network name
in the first field and the Remote LU Name associated with the DRDA server
database in the second field. For this example, use
SPIFNET.NYX1.
- Select Supports parallel sessions and No session level
security.
- Click on OK, then DONE.
- Select Local LU:
- From the APPC menu, select Local LUs.
- In the Local Nodes box, select the node you configured
above.
- In the Configured LUs box, select NEW.
- For the APPC LU alias, enter your Independent LU Name; for this example,
it is NYX2GW01. You may optionally enter a description for
the Local LU.
- Make sure that the Full Network Name fields contain your
Network Name and your Independent LU Name. The LU number should be
000 for an independent LU.
- Change the Session Limit parameter to 030.
- Make sure that you have selected the radio buttons to indicate that this
LU is in the pool of default LUs.
- Move the Remote LU you configured above from the Other Remote
LUs box to the Partner LUs box.
- Select Modes.
- Move the IBMRDB mode from the Other Modes box to the
Associated Modes box.
- Click on OK, then OK again, then
DONE.
- Select the Symbolic destination name :
- Select APPC->Sym Dest Name.
- Select NEW.
- Enter the Symbolic Destination Name you want to associate with the DB2RA
server database and click on OK. You may optionally enter a
description. This name must match the sym_dest_name value you use to
catalog the APPC node.
- For the Partner LU type, make sure that Alias is
selected.
- In the Partner LU box, ensure that the Remote LU you
configured above is highlighted.
- In the Mode Name box, highlight IBMRDB.
- For the Partner TP name, use NYSERVER. In
this example it is an Application TP.
- For the Partner LU type, make sure that Alias is
selected.
- Click on Security and choose none (This does not mean that you
will have no security; you can specify the security type later, in the node
directory).
- When done, click on OK, then OK, then
DONE.
- Saving your configuration:
- From the File menu, select Save.
- Select Update running configuration file, then click on
OK. This saves your new configuration as the default,
running configuration.
- Starting the Interface Systems Cleo Subsystem
- To start the Cleo subsystem, issue /usr/bin/comstart.
Use /usr/bin/comstop to stop Cleo SNA. To start and stop
individual SNA resources, including resources not configured for autostart,
use the Cleo management utilities /usr/bin/commanage or
/usr/bin/cxmanage.
|
Wait 30 - 60 seconds after issuing comstart before invoking
commanage. This will allow automatic links, connections, and
sessions to become active before you start the management utilities.
|
- Using the Cleo SNA Text Configuration Utility
-
The following section provides a working example of the SNA configuration
on a DB2 for SCO OpenServer client to support communications with a server
workstation.
Notes:
- The values provided are for the example only; you must substitute values
that are appropriate for your operating environment.
- Get the correct values from your network administrator.
- A worksheet is available in Table 20 to assist you in gathering the information.
There is one configuration file which is read by the server on
start-up. This configuration file has a default name of
/usr/lib/cleo/com.cfg. The configuration file defines the SNA
resources and operating characteristics through a set of configuration
directives. Cleo supplies a binary text conversion utility to allow
inspection and manipulation of the SNA configuration files directly.
This utility is described in the Cleo Text Configuration Utilities
Guide. Only experienced users should use this method to modify a
configuration. This section describes the text configuration
file.
|
It is a good idea to back up your configuration file to protect against
inadvertent data loss.
|
To use the APPC protocol, you should specify a number of configuration
directives in the configuration file. Assuming a token ring LAN, you
should specify the following configuration directives:
- [TR_LINK]
-
- [TR_CONN]
-
- [TR_USAGE]
-
This entry links together the TR_LINK and NODE entries, and describes how
the local node will control and interact with the link.
- [APPC_MODE]
-
- [APPC_REMOTE_LU]
-
- [APPC_LOCAL_LU]
-
- [NODE]
-
- [SYM_DEST_NAME]
-
See Table 19 for a brief description of the parameters for each directive listed
above.
The following is an example configuration file containing the configuration
directives. See the Interface Systems Cleo Administration
Guide for more information about configuration and administration of
Cleo SNA resources.
; *****************************************************************************
; Cleo Binary to Text Configuration Utility
; Copyright (c) 1989 - 1995 Interface Systems, Inc.
; Binary Configuration = com.cfg
; Security File = com.sec
; Configuration type = Client/Server
; File version = 100.20
; *****************************************************************************
; *****************************************************************************
; Diagnostics Record (Mandatory)
; *****************************************************************************
[DIAGNOSTICS]
connection = "" ; Name of network mgt connection
UCF_user = "" ; User ID for UCF commands
error_log = "/usr/lib/cleo/com.err"
; Error log file
audit_log = "/usr/lib/cleo/com.aud"
; Audit log file
audit_level = 6 ; Detailed problem analysis
send_overfl = No ; Send RTM when response counter max
send_end = No ; Send RTM at end of session
stop_timer = screen ; Data first reaches the screen
boundary_1 = 0.5 ; RTM histogram time boundaries
boundary_2 = 1.0
boundary_3 = 2.0
boundary_4 = 5.0
pc_error_log = "c:\com.err" ; PC client error log file
pc_audit_log = "c:\com.aud" ; PC client audit log file
; *****************************************************************************
; Local Node Record
; *****************************************************************************
[NODE]
name = "NYX1" ; Local Node Name
description = "local node"
; Description of Local Node
network = "SPIFNET" ; Node Network Name
; *****************************************************************************
; Token Ring Link Record
; *****************************************************************************
[TR_LINK]
name = "TOKLINK" ; Name
description = "Token-Ring Link"; Description
device_name = "SNA_TR ; Name of device file for link
adaptor = "net1" ; Name of device file for adaptor
port = 0 ; Adaptor port
; *****************************************************************************
; Token Ring Link Usage Record
; *****************************************************************************
[TR_USAGE]
node = "NYX1" ; Node name
link = "TOKLINK" ; Link name
incoming = Yes ; Incoming calls accepted
max_conn = 10 ; Maximum number of connections
local_sap = 04 ; Local SAP address
; *****************************************************************************
; Token Ring Connection Record
; *****************************************************************************
[TR_CONN]
name = "HOST0001" ; Name of connection
node = "NYX1" ; Name of node
(THIS NODE NOT THE REMOTE COMPUTER)
description = "Token-Ring connection"
; Description
remote_end = host ; Remote end is host
activation = initially ; Initially active
node_send = "05D.51902" ; Node id to send
node_rcv = "05D.00000" ; Node id to receive
control_point = "CAIBMOML.NYX1" ; Fully qualified control point name
remote_address = 400009451902 ; Address of remote TR network
remote_sap = 04 ; Remote SAP address
retry_limit = 2 ; Retry limit
rcv_ack_limit = 2 ; Receive acknowledgment threshold
send_ack_limit = 1 ; Unacknowledged send threshold
max_btu = 1929 ; Maximum BTU length
link = "TOKLINK" ; link
; *****************************************************************************
; APPC Mode Record
; *****************************************************************************
[APPC_MODE]
name = "IBMRDB" ; Mode name
mode_ID = 0 ; Unique Mode ID
description = "IBMRDB to HOST" ; Description
connection = "HOST0001" ; Connection used by this mode
priority = high ; Mode is High Priority
session_limit = 8 ; Mode Session Limit
MCW = 4 ; Min Conwinner Sessions
partner_MCW = 4 ; Partner Min Conwinner Sessions
auto_act = 4 ; Auto activated sessions
min_sendRU = 256 ; Min Send RU size
max_sendRU = 4096 ; Max Send RU size
send_pace = 4 ; Send Pacing count
min_rcvRU = 256 ; Min Receive RU size
max_rcvRU = 1024 ; Max Receive RU size
rcv_pace = 4 ; Receive Pacing count
; *****************************************************************************
; APPC Remote LU Record
; *****************************************************************************
[APPC_REMOTE_LU]
alias = "NYX1GW01" ; LU Alias
description = ""
; Text description of LU
net_name = "SPIFNET" ; LU Network Name
LU_name = "NYX1GW01" ; Name of LU
SSCP_Alias = "NYX1GW01" ; SSCP LU Alias
parallel_sess = Yes ; Parallel Sessions supported
conv_sec = no ; LU uses conversation level security
session_sec = none ; No Session Level Security
; *****************************************************************************
; APPC Local LU Record
; *****************************************************************************
[APPC_LOCAL__LU]
alias = "NYX2GW01" ; LU Alias
node = "NYX2" ; Local Node
description = "local lu" ; Text description of LU
net_name = "SPIFNET" ; LU Network Name
LU_name = "NYX2GW01" ; Name of LU
LU_number = 0 ; LU Number
session_lim = 20 ; Session Limit
default_LU = Yes ; LU in pool of Default LUs
local_use = Yes ; LU can be used locally
syncpoint = No ; LU supports syncpoint sessions
conv_sec = Yes ; LU uses conversation level security
preval_sec = Yes ; LU can prevalidate security
partner_LU = "NYX1GW01, 0" ; List of Partner LUs and Modes
; *****************************************************************************
; Symbolic Destination Name Record
; *****************************************************************************
[SYM_DEST_NAME]
name = "DB2CPIC" ; CPI-C symbolic destination name
description = "" ; Description of sym dest name
partner_type = application ; Application TP partner
partner_name = "NYSERVER" ; Partner TP name
; DB2DRDA or x'07F6C4C2' on MVS,
; x'07F6C4C2' on OS/400,
; RDB_NAME for VSE or VM.
partner_LUtype = alias ; LU name is an alias
partner_LU = "NYX1GW01" ; Partner LU name
mode = "IBMRDB" ; Mode name of mode used
conv_sec = same ; (could be program) No conversation security
You need to customize the APPC configuration for the client. The
following list gives the APPC profiles that you will need to update on your
client workstation before you can access a DB2 server using APPC.
- Link Profile
- Station Profile
- Local LU Profile
- Remote LU Profile
- Mode Profile
- Symbolic Destination Profile
The following section provides a working example of the SNA configuration
on a DB2 for SINIX client to support communications with a server
workstation.
Notes:
- The values provided are for the example only; you must substitute values
that are appropriate for your operating environment.
- Get the correct values from your network administrator.
- A worksheet is available in Table 20 to assist you in gathering information.
There is one configuration file that is read by the TRANSIT Server on
start-up. This configuration file has a default name of
/opt/lib/transit/KOGS/conf.nuc. The configuration file defines
the SNA resources and operating characteristics through a set of configuration
directives.
The following is an example configuration file containing the configuration
directives.
XLINK tok0.001, //Link name
ACT = AUTO, //Activation
TYP = LAN, //Connection type
XID = 05D27946, //Node ID
CPNAME = CAIBMOML.OMXTXL, //Control point
CONFSTR = /opt/lib/llc2/conf.str, //Confstr
DEVICE = tr0, //Device
SSAP = 04 //SSAP
XPU JAGUAR, //Station name
TYP = PEER, //Type
CONNECT = AUTO, //Connection setup
DISCNT = AUTO, //Connection shutdown
LINK = tok0.001, //Link name
NVSCONNECT = DYNAMIC, //NVS connect
MAXDATA = 265, //Segment size
XID = 05D27946, //Node ID
CPNAME = CAIBMOML.OMXTP909, //Control point
ROLE = NEG, //Station role
PAUSE = 3, //Pause
RETRIES = 10, //Retries
DMAC = 10005AA8E208, //DMAC
DSAP = 04, //DSAP
RWINDOW = 7 //Window
XLU OMXTXL, //Name
TYP = 6, //LU type
PUCONNECT = APHSTART, //Connection
CTYP = PUBLIC, //Coordinate Type
SESS-LMT = 3, //Session limit
SESS-CTR = IND, //Session control
NETNAME = CAIBMOML.OMXTXL, //Network name
PAIR = OMXTP909 IBMRDB //LU pair
XRLU OMXTP909, //Remote LU name
NETNAME = CAIBMOML.OMXTP909, //Network name
PU = JAGUAR //Station name
XMODE IBMRDB, //Mode name
SESS-MAX = 20, //Session Max
SESS-LOS = 10, //Session Loser
SESS-WIN = 10, //Session Winner
SESS-AUTO = 5, //Session Auto
SRU-MAX = 87, //RU size Send
RRU-MAX = 87, //RU size Recv
PAC-SEND = 4, //Pacing Send
PAC-RCV = 4, //Pacing Recv
IDLETIME = 0 //Idle time
XSYMDEST CPICSND, //SD name
RLU = OMXTP909, //RLU name
MODE = IBMRDB, //Mode name
TP = CPICRCV, //TP name
TP-TYP = USER, //Type
SEC-TYP = NONE //Security
XEND
You need to customize the APPC configuration for the client. The
following list gives the APPC profiles that you will need to update on your
client workstation before you can access a DB2 server using APPC.
- PARTNER LU Profile
- MODE Profile
- CP Profile
- TRLINE Profile
- DLC Profile
- LU Profile
You also have to create a file containing the CPI-C side information
representing the symbolic destination name.
You can use vi or your favorite editor to create the
configuration files.
This file must be placed in the application's path for a
standalone DB2 Connect for Solaris system. However, if DB2 Connect for
Solaris is being used as a gateway, in order for DB2 agents to be able to
access it, the file should be in either:
- $HOME/sqllib/adm or
- $HOME/sqllib/bin
| Note: | The name of the CPIC side file must be the same as the Symbolic destination
name specified in the DB2 node directory on the DB2 Connect for Solaris
system.
|
Sample CPIC side file
The file name must be the same as the Symbolic destination name specified
in the DB2 node directory for the server.
# CPIC Side File information
#
PTNR_LU_NAME=NYX1GN01
MODE_NAME=IBMRDB
TP_NAME= NYSERVER
SECURITY=NONE
This file is called sunpu2.config, and it must be placed
in /opt/SUNWpu21, or the directory where SunLink SNA PU 2.1
Server is installed.
Figure 1. Sample Solaris PU 2.1 SNA Client Configuration File
// SunLink SunLU6.2/SunPU2.1 SNA Server Sample Configuration
// Token Ring Peer-to-Peer System A @(#)sunlu62.a.tr
//
// The physical connection is a Token Ring interface adapter.
CP NAME=NYX2 // Local name (8 char max)
NQ_CP_NAME=SPIFNET.NYX12 // Network Qualified Name
;
TRLINE NAME=MAC1 // SunLink specific name
SOURCE_ADDRESS=x'400011527509' // sysA_mac_addr for Sun machine
;
DLC NAME=HOSTLINK // User defined name (8 char max)
LINK_NAME=MAC1 // Line name this station is on
LCLLSAP=x'04' // Local Link Service Access Point
RMTLSAP=x'04' // Remove Link Service Access Point
RMTMACADDR=x'40005AA8B532' // sysB_mac_addr
TERMID=x'07127509' // XID negotiation
;
LU NAME=NYX2GW01 // Local name (8 char max)
NQ_LU_NAME=SPIFNET.NYX2GW01 // Network Qualified Name
SESS_LMT=50 // Max LU sessions
LUTYPE=6.2
;
PTNR_LU NAME=NYM2DB2 // Partner LU name(8 char max)
LOC_LU_NAME=NYX1GW01 // Associated Local LU
NQ_LU_NAME=SPIFNET.NYM2DB2 // Network Qualified Name
;
MODE NAME=IBMRDB // Mode Name (8 char max)
DLC_NAME=HOSTLINK // Associated DLC
PTNR_LU_NAME= // Associated Partner LU
LCL_MAX_SESS_LMT=30 // Max Session Limit
MIN_CW_SESS=15 // Min Conwinners
MIN_CL_SESS=15 // Min Conlosers
;
|
You may need to create an entirely new configuration file or customize
an existing one. This section assumes that you are creating a new
configuration file, but if you are customizing an existing one the steps are
similar. You need to perform the following configuration steps:
- Configure Node
- Configure Devices
- Configure Connections
- Configure Transaction Program
- Configure Partner LU
- Configure Mode
- Configure Local LU 6.2
- Configure CPI-C Side Information
To begin, perform the following steps:
- Click on the Start push button, and select
Programs->IBM Communications Server->SNA Node
Configuration.
- Select File->New to create a new configuration file,
as used in this example, or you can select File->Open to
select, open, and modify an existing configuration profile.
- Select Scenarios->CPI-C, APPC, or 5250 Emulation, or
you can select Scenarios->Advanced when creating a new
configuration file or modifying an existing one.
- Configure Node
-
To configure the node, do the following (this example is for an End
Node):
- Select the Configure Node configuration option, and click on
New. The Define The Node notebook appears.
- Complete the Basic notebook page as follows. Use the
values that you recorded on your worksheet, for example:
- Fully qualified CP name
- SPIFNET.NYX2 (19) and (20)
- CP alias
- We suggest you use NYX2, the same value as (20)
- Local Node ID
- 05D for the Block ID (the first three digits of (21)),
and 27510 for the Physical Unit ID (the last five digits of
(21)).
- Node Type
- End Node was specified in this example.
- Click on OK to save the node definition and return to the
Communications Server SNA Node Configuration window.
- Configure Devices
-
To configure devices, do the following (this example used a LAN DLC):
- Select the Configure Devices configuration option.
- Select the appropriate DLC for your environment. In this example,
LAN was used.
- Click on New. The Define a LAN Device notebook
appears.
- All the fields on the Basic notebook page were allowed to
default in this example. The same was true for the Advanced
and Performance notebook pages
- Click on OK to save the node definition and return to the
Communications Server SNA Node Configuration window.
- Configure Connections
-
To configure the LAN connection, do the following:
- Select the Configure Connections configuration option, with
your DLC also selected (LAN in this example).
- Click on New. The Define a LAN Connection notebook
appears.
- Complete this notebook page as follows. Use the values that you
recorded on your worksheet, for example:
- Link Station Name
- Use any unique and meaningful value, such as LINKNYX1.
- Device name
- Use the value that already appears. It was selected when you
configured the device in the previous step.
- Destination Address
- 40005AA8B532 (16)
- Remote SAP
- Was left to default to 04 in this example.
- Select the Security notebook tab, and set the Adjacent CP
name to SPIFNET.NYX1, corresponding to worksheet items
(17) and (13).
- Click on OK to save the connection definition and return to the
Communications Server SNA Node Configuration window.
- Configure Transaction Program
-
No action is required.
- Configure Partner LU
-
To configure the partner LU, do the following:
- Select the Configure Partner LU configuration option, and click
on New. The Define a Partner LU 6.2 notebook
appears.
- Complete the Basic notebook page as follows. Use the
values that you recorded on your worksheet, for example:
- Partner LU Name
- SPIFNET.NYX1GW01 (17) and (18)
- Partner LU Alias
- We suggest you use NYX1GW01, the same value as (18)
- Fully Qualified CP Name
- SPIFNET.NYX1 (17) and (13)
- Click on OK to save the partner LU definition and return to the
Communications Server SNA Node Configuration window.
- Configure Mode
-
To configure the mode, do the following:
- Select the Configure Mode configuration option, and click on
New. The Define a Mode notebook appears.
- Complete the Basic notebook page as follows. Use the
values that you recorded on your worksheet, for example:
- Mode name
- IBMRDB (26)
- PLU session mode limit
- Was allowed to default (32).
- Minimum contention winner sessions
- Was allowed to default (16).
- Select the Advanced notebook page. Usually all of these
values can be allowed to default. However, you may need to verify or
even change the Maximum PIU size for this workstation. For example, if
the connection to the server will use an Ethernet adapter, the maximum
Ethernet frame size is 1536 bytes, and this would require a maximum RU size no
greater than 1529 bytes.
- Click on OK to save the mode definition and return to the
Communications Server SNA Node Configuration window.
- Configure Local LU 6.2
-
To configure the local LU, do the following:
- Select the Configure Local LU 6.2 configuration option,
and click on New. The Define a Local LU 6.2 notebook
appears.
- Complete the Basic notebook page as follows. Use the
values that you recorded on your worksheet, for example:
- Local LU Name
- NYX2GW01 (27)
- Local LU alias
- We suggest you use the same value as for item (27)
- LU session limit
- Leave this set to 0 (permits up to 64K sessions)
- Click on OK to save the node definition and return to the
Communications Server SNA Node Configuration window.
- Configure CPI-C Side Information
-
To configure the CPI-C Side Information, do the following:
- Select the Configure CPI-C Side Information configuration
option, and click on New. The Define CPI-C Side Information
notebook appears.
- Complete the Basic notebook page as follows. Use the
values that you recorded on your worksheet, for example:
- Symbolic Destination Name
- NYSERVER (23)
- Mode name
- Select IBMRDB, the same value as (26)
- Use Partner LU Name or Use Partner LU Alias
-
Click the radio button that selects which of these you will use.
Either specify the fully-qualified partner LU name
SPIFNET.NYX1GW01 (the same value as worksheet item
(22)), or select the Partner LU alias that you defined earlier (the
same value as worksheet item (18) in this example).
- TP Name
- NYSERVER (24)
- Complete the Security notebook page as follows. Use the
values that you recorded on your worksheet, for example:
- Conversation Security
- Specify NONE (25)
- Click on OK to save the CPI-C Side Information definition and
return to the Communications Server SNA Node Configuration window.
To complete the configuration file, from the Communications Server SNA Node
Configuration window:
- Select File->Save As and specify the configuration
file name of your choice, for example nyserver.acg.
Indicate whether this configuration file is to become the default for this
workstation.
- Close the Communications Server SNA Node Configuration window.
- Use Start->Programs->IBM Communications
Server->SNA Node Operations to open the Communications
Server Node Operation window.
- Select Operations->Start Node->Open to
start the node with the new configuration file.
You need to customize the APPC configuration for the client. The
following list gives the APPC profiles that you will need to update on your
client workstation before you can access a DB2 server using APPC.
- Server Properties
- Local LU Properties
- Mode Properties
- Connection Properties
- Remote LU Properties
- CPI-C Symbolic Destination Name Properties
To begin, perform the following steps:
- Click on the Start push button, and select
Program->SNA
- Double-click on the SNA Server Admin icon. The SNA
Server Admin window opens.
|
By default, the Servers and Connections window opens. If it does
not, double-click on the Servers and Connections icon.
|
- Server Properties
-
To specify parameters for an SNA Server that will be used for LU 6.2
(APPC), do the following:
- In the Servers and Connections window, select the server (named SERVER in
the example).
- Select Services->Properties. The Server
Properties window opens.
- Enter the values you filled in on Table 20 as follows:
- Network Name
- (19)
- Control Point Name
- (20)
- Local LU Properties
-
To assign a local APPC LU to the Server, perform the following steps:
- In the Servers and Connections window, select the server.
- Select Services->Assign LUs. The Insert LU
window opens.
- In the Insert LU window, select APPC (Local).
- Click on OK. The New APPC LU Properties window
opens.
- Make sure that the Independent radio button is selected.
- Enter the values you entered in on Table 20 as follows:
- LU Alias
- (27)
- Network Name
- (19)
- LU Name
- (27)
- Select the Enable Automatic Partnering check box, if it is not
already selected.
- Select the Member of Default Outgoing Local APPC LU Pool check
box, if it is not already selected.
- Click on OK. The new LU is added to the window.
- Mode Properties
-
You can use an IBM-defined mode, or add a new mode that is appropriate for
the application. Ensure that the values match between your client and
server.
To configure a mode for the APPC LU, perform the following steps:
- In the Servers and Connections window, select the local LU with which the
mode will be associated.
- Click on Services->Properties.
Based on whether the LU is local or remote, either the APPC LU Properties
window or the New APPC LU Properties window opens.
- Click on the Partners... push button. The LU
6.2 Partner LUs window opens.
- Click on the Modes... push button. The APPC Mode
Properties window opens.
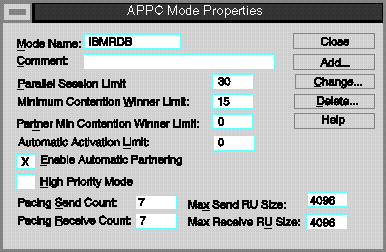
- Use the following suggested value:
- Mode Name
- IBMRDB (26)
- Select the Enable Automatic Partnering check box, if it is not
already selected.
- Ensure that the High Priority Mode check box is not
selected; if it is, clear the check box.
|
The rest of the values in our example are arbitrary. The values for
items such as Parallel Session Limit and Minimum Contention
Winner Limit are for tuning purposes. See the online help for SNA
Server for guidance on setting these values.
|
- Click on the Add push button to add the mode.
- Click on the Close push buttons until you return to the APPC LU
Properties window.
- Click on the Cancel push button to return to the Servers and
Connections window.
- Connection Properties
-
To configure settings for a new connection, do the following:
- In the Servers and Connections window, select the server that you
want.
- Select Services->New Connection. The Insert
Connection window opens.
- In the Insert Connection window, select the type of connection you
want. Our example uses 802.2. See the online
help for information on the other available choices.
- Click on OK. The Connection Properties window
opens. Use the following values:
- Connection Name
- LINKNYX1 (15)
- Link Service
- SnaDlc1
- Remote End
- Peer System radio button
- Activation
- On Demand radio button
- Allowed Directions
- Outgoing Calls check box.
- Click on the Setup push button.
The 802.2 Setup window opens.
- Use the following values:
- Remote Network Address
- 40005AA8B532 (16)
- Local Node ID
- 05D 27510 (21)
- Network Name
- SPIFNET (19)
- Control Point Name
- NYX1 (13)
- Click on OK to save your work and return to the Connection
Properties window.
- Click on OK.
- Remote LU Properties
-
To assign a remote APPC LU to a connection do the following:
- In the Servers and Connections window, select the connection that you
want.
- Select Services->Assign LUs.
The Insert LU window opens.
- In the Insert LU window, select APPC Remote.
- Click on OK. The New APPC Remote LU Properties window
opens.
- Fill in the values for your system. For example.
- LU Alias
- NYX1GW01
- Network name
- SPIFNET (17)
- Remote LU name
- NYX1GW01 (18)
- Make sure the Supports Parallel Sessions and the Enable
Automatic Partnering check boxes are selected.
- Click on OK.
- CPI-C Symbolic Destination Name Properties
-
To configure the properties for CPI-C, do the following:
- Select Options->CPI-C. The Configure CPI-C
Names window opens.
- Click on the Add push button. The CPI-C Symbolic
Destination Name Properties window opens.
- Use the values that you recorded on your worksheet. For
example:
- Name
- NYSERVER (23)
- SNA Service TP
- this field will be blank
- Fully Qualified
- SPIFNET.NYX1GW01(17) and (18)
- Mode Name
- IBMRDB (26)
- Conversation Security
- By default, None is selected. You will specify the
conversation security type later.
- Click on OK to save your work and return to the Connection
Properties window.
- Click on the Close push button to close the Configure CPI-C
Names window and return to the Servers and Connections window.
You must add an entry to the client's node directory
to describe the remote node.
This entry specifies the chosen alias (Node_name), Symbolic
destination name (sym_dest_name), and the APPC Security type
(security_type) to be used for the APPC connection.
To catalog the APPC node, perform the following steps:
- Log on to the system as a user with System Administrative (SYSADM) or
System Controller (SYSCTRL) authority.
- If you are using UNIX, set up the instance environment and invoke the DB2
command line processor as follows:
- Run db2profile or db2cshrc as follows:
. INSTHOME/sqllib/db2profile (for Bourne or Korn shell)
source INSTHOME/sqllib/db2cshrc (for C shell)
where INSTHOME is the home directory of the instance
- Start the DB2 command line processor by issuing the db2
command.
- Catalog the node by issuing the following commands in the command line
processor:
catalog appc node Node_name remote sym_dest_name security security_type
terminate
For example, to catalog a remote database server with the Symbolic
destination name NYSERVER on the node called db2node, using
APPC Security type none, use:
catalog appc node db2node remote NYSERVER security none
terminate
|
If you need to change values that were set with the catalog node
command, first run the uncatalog node command in the command line
processor as follows:
uncatalog node Node_name
Recatalog the node with the value that you want to use.
|
Before a client application can access a remote database, the database must
be cataloged on the server node and on any client nodes that will connect to
it. When you create a database, it is automatically cataloged on the
server with the Database alias (Database_alias) the same as the Database name
(Database_name). The information in the database directory, along with
the information in the node directory, is used on the client to establish a
connection to the remote database.
To catalog a database on the client, perform the following steps.
- Log on to the system as a user with System Administrative (SYSADM) or
System Controller (SYSCTRL) authority.
- Fill in the Your Value column in the following
worksheet.
Table 21. Parameter Values for Cataloging Databases
| Parameter
| Description
| Sample Value
| Your Value
|
| Database name (Database_name)
| The Database alias (Database_alias) of the remote
database. When you create a database, it is automatically cataloged on
the server with the Database alias name (Database_alias) the same as the
Database name (Database_name).
| sample
|
|
| Database alias (Database_alias)
| An arbitrary local nickname for the remote database, on the
client. If you do not provide one, the default is the same as the
Database name (Database_name). This is the name that you use
when connecting to a database from a client.
| tor1
|
|
| Node name (Node_name)
| The name of the node directory entry that describes where the database
resides. Use the same value for Node name (Node_name) that you
used to catalog the node in the previous step.
| db2node
|
|
- If you are using UNIX, set up the instance environment and invoke the DB2
command line processor as follows:
- Run db2profile or db2cshrc as follows:
. INSTHOME/sqllib/db2profile (for Bourne or Korn shell)
source INSTHOME/sqllib/db2cshrc (for C shell)
where INSTHOME is the home directory of the instance
- Start the DB2 command line processor by issuing the db2
command.
- Catalog the database by issuing the following commands in the command line
processor:
catalog database Database_name as Database_alias at node Node_name
terminate
For example, to catalog a remote database called sample so that
it has the alias tor1, on the node db2node, use:
catalog database sample as tor1 at node db2node
terminate
|
If you need to change values that were set with the catalog
database command, first run the uncatalog
database command in the command line processor as
follows:
uncatalog database Database_alias
Recatalog the database with the value that you want to use.
|
When the configuration of the client is complete, use the
following steps to verify that you can access data from a remote
database:
|
You will need to connect to a remote database to test the
connection. If you do not have a database on the server, create the
sample database on the server to test the connection. Refer to the Quick Beginnings manual for more information.
|
- Start the database manager by issuing the db2start command on
the server (if it was not automatically started at boot time).
- Issue the following command in the client's Command Center or command
line processor to connect the client to the remote database:
connect to Database_alias user userid using password
The values for userid and password must be valid for the
system on which they are authenticated. By default, authentication
takes place on the SERVER. If the database manager is configured for
CLIENT authentication, the userid and password must be valid
on the client.
If the connection is successful, you will get a message showing the name of
the database to which you have connected. You are now able to retrieve
data from that database. For example, to retrieve a list of all the
table names listed in the system catalog table, enter the following SQL
command in the Command Center or command line processor:
"select tabname from syscat.tables" (for UNIX-based platforms)
select tabname from syscat.tables (for other platforms)
When you are finished using the database connection, issue the connect
reset command to end the database connection.
If the connection fails, check the following items:
At the server:
- The DB2COMM registry parameter includes the value
appc.
- The Transaction program name (tpname) parameter was updated
correctly in the database manager configuration file (or the admin server
configuration file, if you are setting up the Administration Server).
- The security service was started (issue the net start
db2ntsecserver command-for Windows NT servers only).
- The database was created and cataloged properly.
- The database manager was stopped and started (issue the db2stop
and db2start commands on the server).
|
If there are problems starting a protocol's connection managers, a
warning message is displayed and the error messages are logged in the
db2diag.log file. The location of this file depends on your
operating system.
- UNIX-based Platforms
- $HOME/sqllib/db2dump directory, where $HOME is home directory of
the instance owner.
- Other Platforms
- x:\sqllib\%db2instance% directory, where x: is the
drive that the client is installed and %db2instance% represents the
DB2 instance.
Refer to the Troubleshooting Guide for information on the db2diag.log file.
|
At the client:
- The node was cataloged with the correct Symbolic destination name
(sym_dest_name).
- The Node name (Node_name), specified in the database directory,
points to the correct entry in the node directory.
- The database was cataloged properly, using the server's
Database alias (Database_alias) that was cataloged when the database
was created on the server, as the Database name (Database_name) on
the client.
After you verify these items, refer to the Troubleshooting Guide if the connection still fails.
[ Top of Page | Previous Page | Next Page | Table of Contents | Index ]
[ DB2 List of Books |
Search the DB2 Books ]